A chart that helps guide your understanding of your dog's behaviour
This flowchart will present an understanding of your dog's behaviour, and whether it relates to the possibility of a medical condition
Complete the flowchart to understand how aggressiveness and anxiety can be managed.
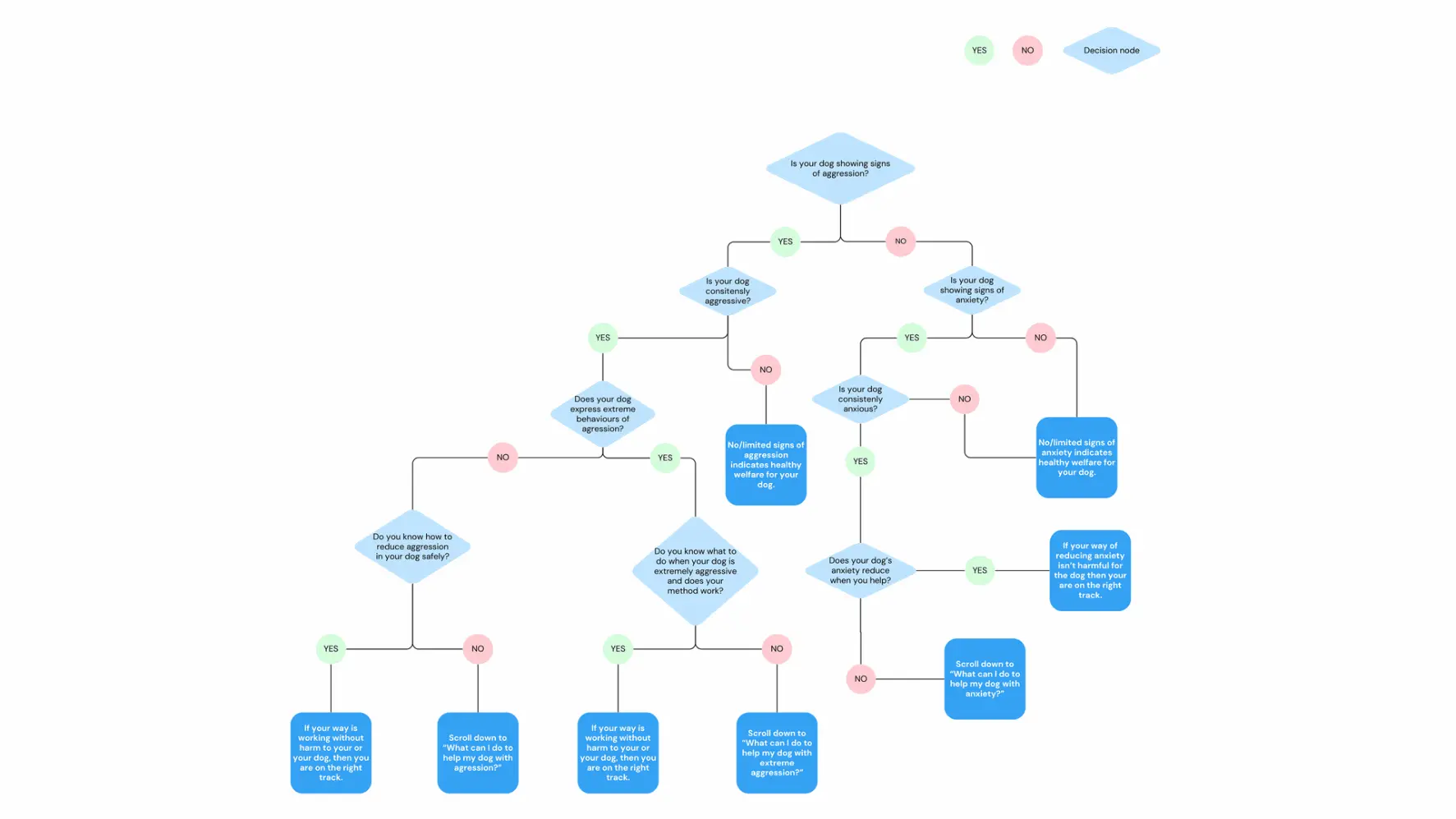
Flowchart Explanation
Below shows the following information to help, based on your result on the flowchart, as well as further explanations on common questions.
Aggression is a way of dogs' communication during an uncomfortable situation. The severity of aggressive behaviour depends on the situation your dog is in and how that situation makes your dog feel. There may be certain places, objects, people, or animals that may trigger your dog's signs of aggression.
Knowing the history of your dog can help with understanding their aggression. If your dog was rescued, there may have been a traumatic experience in your dog's past that triggers aggression. If you have had your dog since they were a puppy, then the aggressive behaviour may have been learnt through environmental factors. Sometimes specific breeds can be considered more aggressive, but this is not the case. Some breeds have specific characteristics that allow there to be a more aggressive response, such as biting. Some breeds, such as Cane Corso, Shepherds, Rottweiler, and American Bulldog, have a stronger jaw; when they bite with the same intention as any other breed, their bite will cause more damage/harm due to this physical characteristic.
In more serious situations, sometimes aggression can be shown to express that your dog is in discomfort. In a serious situation, this may indicate that your dog is in pain due to a medical condition; this could be brain inflammation or hypothyroidism.
Severe aggression in dogs depends on the situation. Your dog may become very aggressive because there is something that has triggered your dog into thinking there is danger. Depending on what or who your dog is being aggressive towards, evaluate the situation and ensure that those around you, including yourself, remain calm and safe.
Your dog may be extremely aggressive due to something or someone that has triggered this behavior. For example, if your dog had a negative experience with cats, this can then cause your dog to become aggressive when they encounter a cat.
Anxiety in dogs is caused by numerous factors, including genetics and experiences. Anxiety can be inherited from the parents. The main reasons for anxiety within dogs are fear, separation, and age-related anxiety.
Loud noises, unknown animals or people, specific objects, and new or strange environments/situations (e.g., vets, car rides) are all triggers that can create fear for your dog.
If you notice your dog becomes uncomfortable when you are separated, then your dog is very likely experiencing separation anxiety. This is when your dog is unable to come to a sense of comfort when you or the family is away, even if it is for a short amount of time. Some symptoms of separation anxiety include defecating in the house, acting recklessly by destroying furniture, and barking.
Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome (CDS) is a condition that leads to a decline in memory, learning, and awareness, leading to confusion and anxiety. This is an age-related condition that sometimes can become a cause of aggression.
Symptoms of anxiety in dogs include drooling, panting, recklessness, depression, excessive barking, pacing, restlessness, repetitive behaviour, and aggression.
It is important not to punish your dog when they are showing signs of aggression. Knowing what to do to ensure you and others, including the dog, are safe, is important. Punishing your dog by yelling, slapping, etc., when they show aggression, can make them think that what they were trying to communicate was diminished, which can lead to future situations where they feel uneasy, and the aggression can become worse as an attempt to voice their discomfort louder.
Knowing what is triggering your dog is very important. Being able to remove the trigger, if possible, can limit the amount of aggressiveness your dog is expressing.
Knowing what triggers anxiety in your dog is crucial to preventing it and improving your dog's general well-being. Exposing your dog gradually to new experiences and environments can help your dog open up within the right amount of time without harming your dog. If there are specific objects that cause your dog to become anxious, try removing them from a place that your dog can see them. If this is not possible, try to gradually allow your dog to come to the sense that the object is not harmful.
If you are thinking of adopting a dog, knowing the breed is beneficial to understanding if it is the right breed for you. Also, knowing what triggers your dog if you are rescuing can allow you to prepare your home to welcome a smooth transition for your dog.
If you know your lifestyle requires you to be away from home for an excessive amount of time, consider that a dog requires daily attention and care. If your lifestyle does not allow you to take your dog with you , make sure you consider this, as keeping your dog in the kennels for a long amount of time can create anxiety within your dog.
Ensure that your dog is exercising by going on walks or trips to the park, depending on what suits your dog better, which improves your dog's mental health, prevents anxiety, and improves their welfare.
Taking a trip to the veterinarian can help your dog be diagnosed and prescribed medication that reduces anxiety. It is important to be able to try and remove anything that causes anxiety in your dog.
If everything you have tried to prevent aggression in your dog is not working to the point where it has become unmanageable and unsafe, consulting with a professional is the best option. Going to the vet or contacting a professional who will be able to help with aggression in your dog will help with the safety of yourself and others.
Taking a trip to see a veterinarian can help understand if the aggression is underlying medical conditions such as brain inflammation or hypothyroidism.